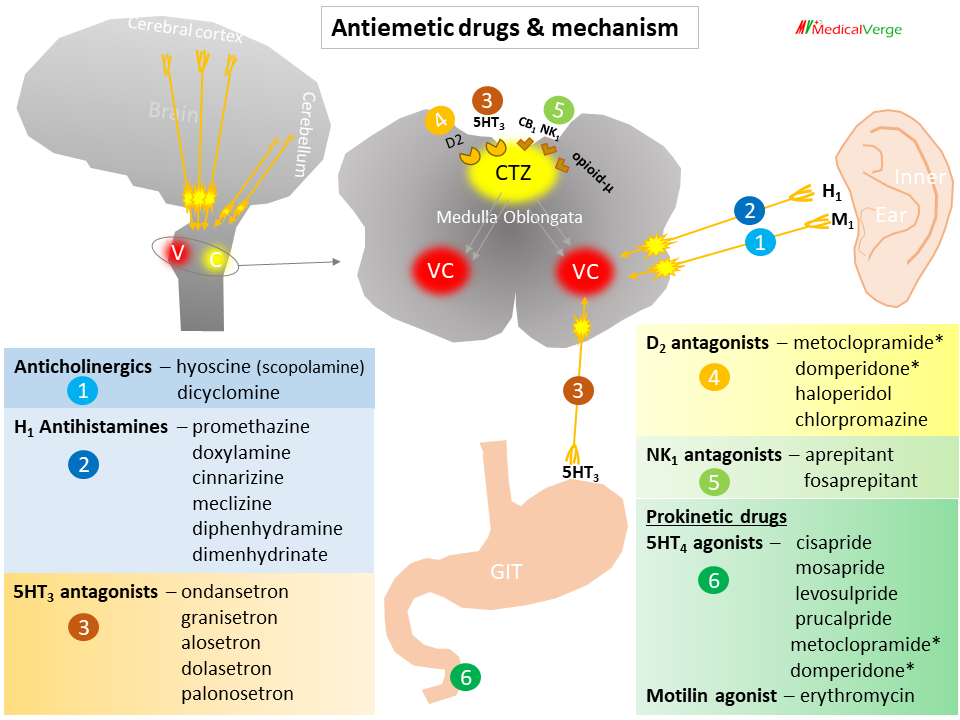
Antiemetics: classification, mechanism and uses/ etiology-based drug selection
Antiemetics are drugs used to prevent vomiting. Vomiting is a protective mechanism of GIT/stomach to expel out undesired or hazardous foods or chemicals. It is an innate protective reflex rather than a disease, while nausea is the sense of vomiting. Sometime undesirable vomiting can occur due to emotional stress, motion sickness, therapeutic drugs like anticancer, […]
Antiemetics: classification, mechanism and uses/ etiology-based drug selection Read More »