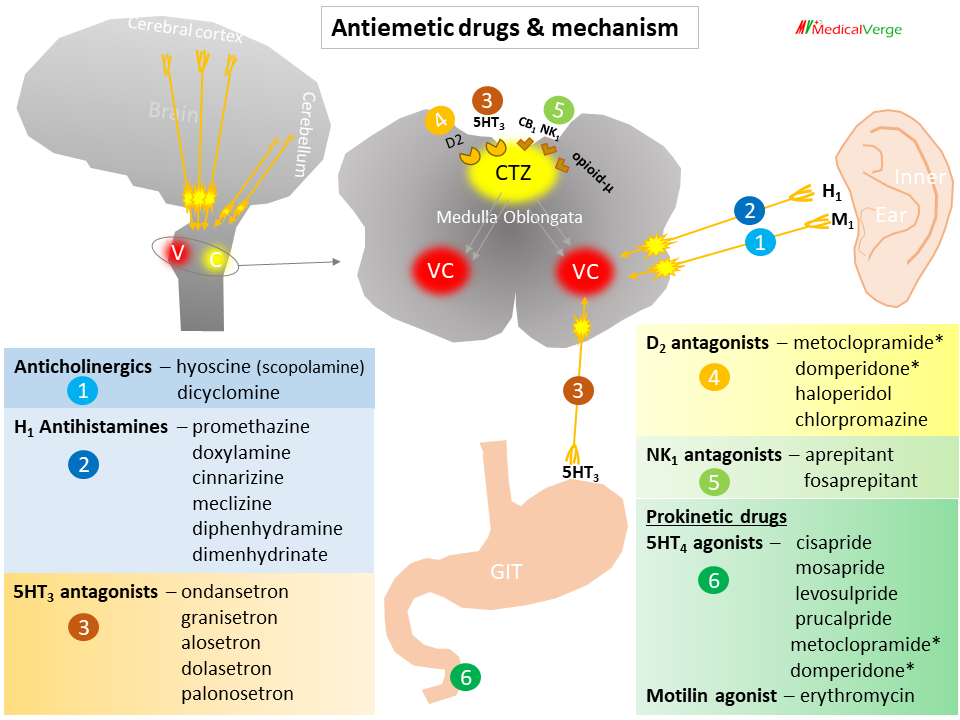
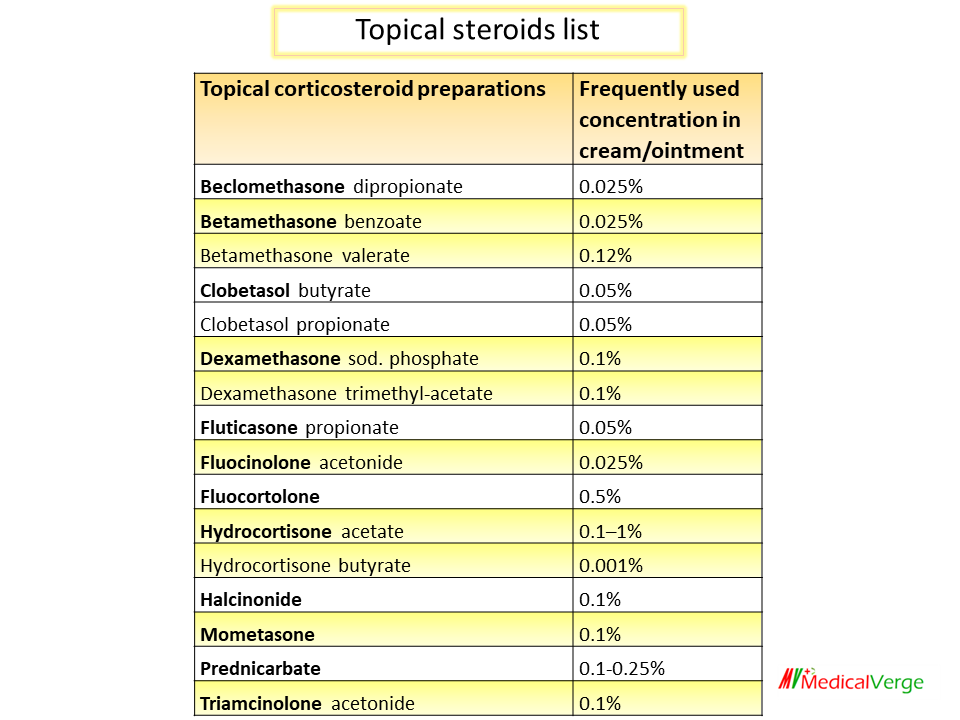
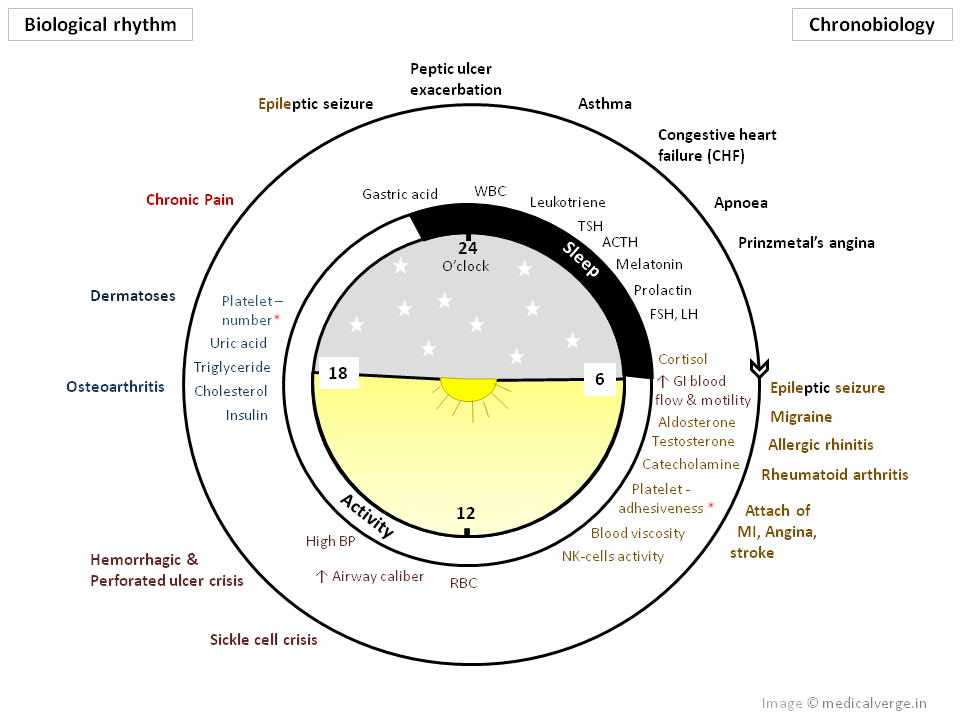
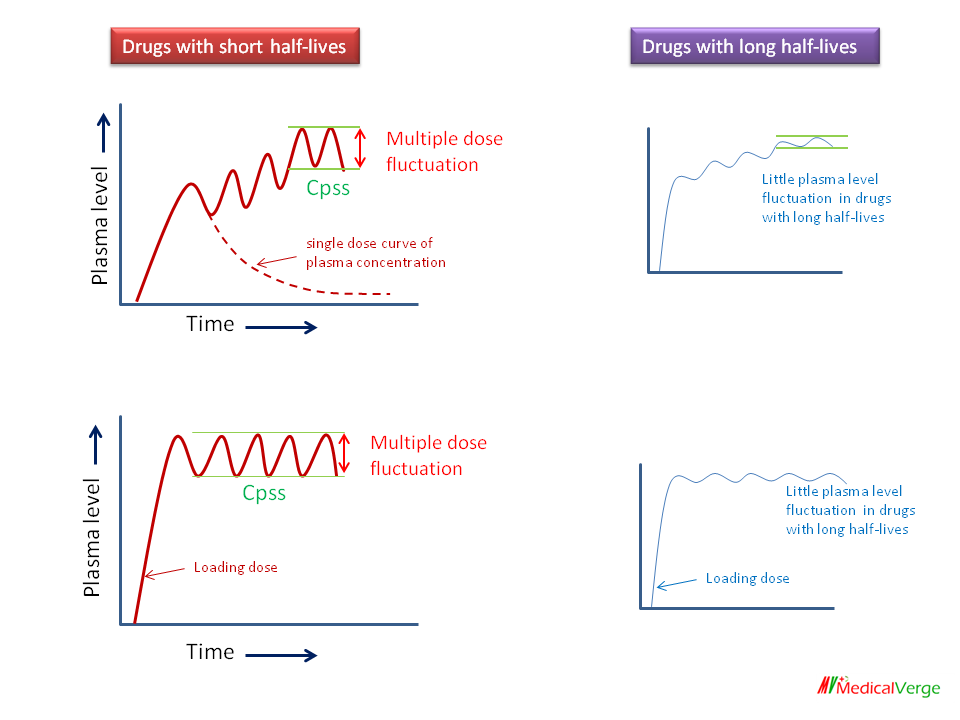
Pharmacokinetics
Introduction Pharmacokinetic is the kinesis (movement) of pharmacological substances (drugs) throughout the body, which includes all phases and processes from entering to leaving the body. It is merely “what the body does with the drug.” Those drug kinetics can be broadly divided into 4 (ADME): If the drug is administered intravenously, there are only three […]