CYP 3A4/5 is the most abundant microsomal enzyme (CYP) and conducts biotransformation of the majority (almost 50%) of drugs. The pace of metabolism is increased by 2–4 fold by the induction of microsomal enzymes (CYP450). Induction takes 4–14 days to reach its peak and is maintained till the inducing agent is being given. The enzymes then gradually regain their original value over a period of 1-3 weeks. Knowing this interaction is crucial for drugs with narrow safety margin.
A drug may be the substrate as well as inhibitor of the same CYP isoenzyme (prolonging plasma half-life) or inducer of same isoenzyme (autoinduction).
A drug may inhibit one isoenzyme while being itself a substrate of another isoenzyme, e.g., quinidine is metabolized mainly by CYP3A4 but inhibits CYP2D6.
Microsomal enzymes
They are found on smooth endoplasmic reticulum primarily in liver, but they are also present in the kidney, intestinal mucosa, and lungs. Microsomal enzymes include monooxygenases, cytochrome P450, UGTs, epoxide hydrolases, etc. Most oxidations, reductions, hydrolysis, and glucuronide conjugation are catalyzed by them. Microsomal enzymes are inducible by drugs and certain dietary constituents.
Non-microsomal enzymes
These are present in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of hepatic cells as well as in other tissues including plasma. The majority of conjugases, amidases, certain flavoproteins oxidases, and esterases are non-microsomal enzymes. Reactions catalyzed are some oxidations and reductions, many hydrolytic reactions and all conjugations except glucuronidation. The non-microsomal enzymes are not inducible.
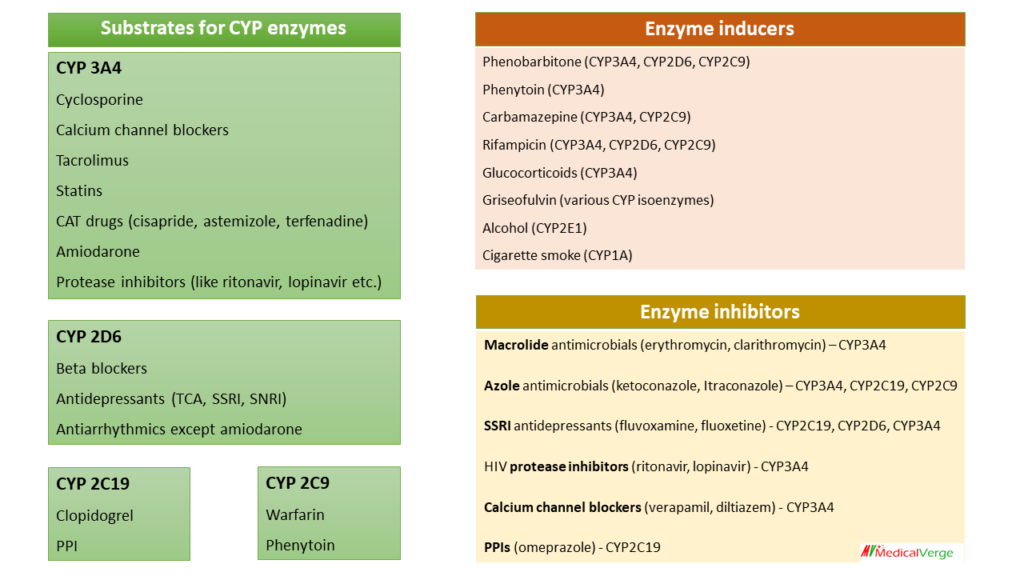
Substrates for CYP enzymes
CYP 3A4
Cyclosporine, CCB
Tacrolimus
Statins
CAT drugs (cisapride, astemizole, terfenadine) – all these withdrawn from market because of QT prolongation
Amiodarone
Navirs (Protease inhibitors like ritonavir, lopinavir etc.)
These can be remember by mnemonic ‘CT SCAN‘.
CYP 2D6
Beta blockers
Antidepressants (TCA, SSRI, SNRI)
Antiarrhythmics except amiodarone
CYP 2C19
Clopidogrel
PPI
CYP 2C9
Warfarin
Phenytoin
CYP Enzyme inducers
Phenobarbitone (CYP3A4, CYP2D6, CYP2C9)
Phenytoin (CYP3A4)
Carbamazepine (CYP3A4, CYP2C9)
Rifampicin (CYP3A4, CYP2D6, CYP2C9)
Glucocorticoids (CYP3A4)
Griseofulvin (various CYP isoenzymes)
Alcohol (CYP2E1)
Cigarette smoke (CYP1A)
CYP Enzyme inhibitors
Macrolide antimicrobials (erythromycin, clarithromycin) – CYP3A4
Azole antimicrobials (ketoconazole, Itraconazole) – CYP3A4, CYP2C19, CYP2C9
SSRI antidepressants (fluvoxamine, fluoxetine) – CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4
HIV protease inhibitors (ritonavir, lopinavir) – CYP3A4
Calcium channel blockers (verapamil, diltiazem) – CYP3A4
PPIs (omeprazole) – CYP2C19
Ciprofloxacin – CYP3A4
Grapefruit juice – CYP3A4
Consequences of CYP enzyme induction
- Decreased intensity or duration of action of drugs that are inactivated by metabolism, e.g., failure of oral contraceptives to prevent pregnancy.
- Increased intensity of action of drugs that are activated by metabolism. Acute paracetamol toxicity is due to one of its metabolites, which manifests at lower dosages in individuals taking enzyme inducers.
- Tolerance may develop, if the drug induces its own metabolism (autoinduction), e.g., carbamazepine, rifampicin.
- Some endogenous substrates (steroids, bilirubin) are also metabolized faster.
- Precipitation of acute intermittent porphyria as a result of enzyme induction, which enhances porphyrin synthesis by derepressing δ-aminolevulenic acid synthetase.
- The dose adjustment of another drug prescribed on a regular basis, such as oral anticoagulants, oral hypoglycemics, antiepileptics, or antihypertensives, may be affected by intermittent usage of an inducer.
Clinical implications
- The ‘boosted’ HIV-protease inhibitor (PI) approach makes use of the potent CYP3A4 inhibitory action of low dose ritonavir to reduce the dose of other PIs like atazanavir, lopinavir, saquinavir given together
- Rifampicin and other enzyme inducers increase the metabolism of PIs, rendering them ineffective.
- Oral contraceptive failure in the context of rifampicin therapy or other enzyme inducers.
- Clopidogrel is a prodrug, become active by CYP 2C19. PPI competitively inhibit 2C19, which prevents clopidogrel from activating and having the desired therapeutic effect.
- Congenital non-hemolytic jaundice is due to deficient glucuronidation of bilirubin. Phenobarbitone hastens clearance of jaundice, by inducing metabolism of bilirubin.